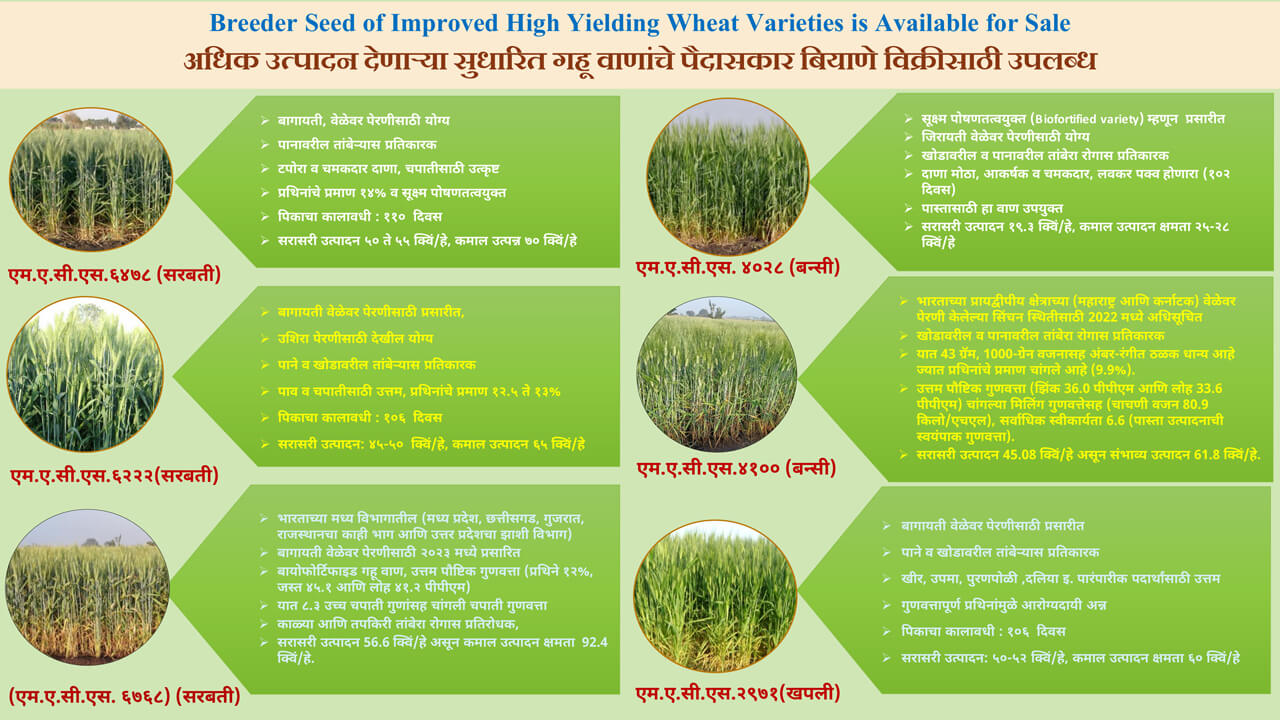
Google Scholar / Social Media
Name : Dr. Chinmoy Patra
Designation : Scientist – E
Brief Background :
Dr. Chinmoy Patra has pursued his undergraduate studies in Pharmaceutical Science from Jadavpur University, Kolkata. He secured All India Rank-1 in Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering (GATE) – 2005 in Pharmaceutical Science. He has received his Master’s degree (M.Tech) fromIIT Kharagpur and was awarded DAAD Fellowship(2006) tocomplete his M.Tech project atTU Dresden, Germany.
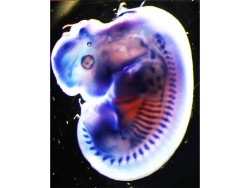
He has pursued his doctoral work under the guidance of Dr. Felix B. Engle atthe Max-Planck-Institute forHeart and Lung Research, Germany. His doctoral work leads to the understanding the role of extracellular matrix molecule nephronectin in cardiac valve development in zebrafish. Subsequently, he worked with Prof. Didier Stanier as a postdoctoral fellow at the MPI for heart and Lung Research, Germany. His research works lead toa number ofpublications in reputed peer reviewed journals like Development, Cardiovascular research, Biomaterials, PNAS USA, Blood, Journal of Neuroscience etc.
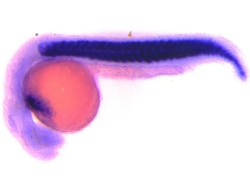
In 2014, Dr. Patra has joined Agharkar Research Institute,Pune and established hislab with the research focus to understand the cellular and molecular regulation behind the cardiovascular development, tissue homeostasis, and heart regeneration using zebrafish as a model organism.
His group has been published in Science, Cell & Bioscience, Thrombosis and Haemostasis, Scientific reports etc. and research work has also been discussed in several news media like The Indian Express, Research Mattersand the Times of India. He has received several prestigious awards like, Max-Planck Partner Group Award, in 2015, Early Carrier Research Award from Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi in 2016, DBT/Wellcome Trust India Alliance Intermediate Fellowship in 2019.
Contact Details :
7743875812 (Mobile)
020-2532-5046 (Telephone)
- From 2018 : Scientist D at the Agharkar Research Institute, Division of Developmental Biology, Pune, INDIA
- 2014-2018: Scientist C at the Agharkar Research Institute, Division of Developmental Biology, Pune, INDIA
- 2012-2014: Post Doctoral fellow with Prof. Didier Stainier. Department of Developmental Genetics, Max-Planck-Institute for Heart and Lung Research, Germany.
- 2010-2012 : Post Doctoral fellow with Prof. Felix B. Engel. Department of Heart Development and Regeneration, MPI for Heart and Lung Research, Germany.
- 2007-2010 : Performed Doctoral thesis work under the guidance of Dr. F.B. Engel at Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research, Germany
Thesis title: Nephronectin regulates cardiac valvedevelopment via BMP4-HAS2 signaling in zebrafish.
(PhD Degree Received-November, 2011) Grade-Very good
Development of an organ or new life is a spectacular process, which is controlled by spatiotemporal gene expression. A considerable part of any tissue is extracellular space, which is filled up with highly complex networks of macromolecules like proteins, proteoglycans etc. as well as relatively simpler molecules such as saccharides and water. Historically the importance of the extracellular matrix (ECM) was as an inert supporting structure to maintain the tissue architecture. However, recent studies from my and other laboratories clearly indicate that ECM components also play major roles during organogenesis, tissue homeostasis, in organ function, in disease, and in regeneration by regulating signalling networks. Thus we can say ECM is the hub of master regulators.
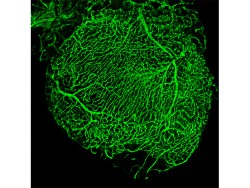
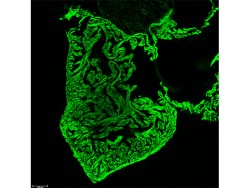
My lab is interested to understand how ECM molecules and adhesion G-protein coupled receptors (aGPCRs) are involved in organ development, tissue homeostasis, organ function and regeneration at the cellular level, using zebrafish as model organism. We investigate our questions utilizing genetic (transgenesis, genome editing with the help of state-of-the-art technology TALEN and CRISPR-Cas), and pharmacological approaches. One of our goals is to understand the crosstalk between different cell types via ECM components during heart development and heart regeneration.
We are looking for enthusiastic, highly motivated students wish to work in the field of cardiovascular biology and genome editing. We also offer scientific training to Masters and Bachelor students.
Key Publications
- Barrodia P, Patra C and Swain RK. EF-hand domain containing 2 (Efhc2) is crucial for distal segmentation of pronephros in zebrafish. Cell & Bioscience (ISSN#2045-3701) 2018; 8:53.
- Patra C*, Kontarakis Z, Kaur H, Rayrikar A, Mukherjee D and Stainier DYR. The zebrafish ventricle: A hub of cardiac endothelial cells for in vitro cell behavior studies. Scientific Reports (ISSN#2045-2322) 2017; 7:2687.
* Corresponding Author
- Mokalled MH, Patra C, Dickson AL, Endo T, Stainier DYR and Poss KD. Injury-induced ctgfa directs glial bridging and spinal cord regeneration in zebrafish. Science (ISSN#1095-9203)2016; 354 (6312):630-634.
- Patra C,Boccaccini AR and Engel FB. Vascularization for cardiac tissue engineering: the extracellular matrix. Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISSN#1538-7836) 2015; 113(3):532-47.
- Patra C, van Amerongen MJ, Ghosh S, Ricciardi F, Sajjad A, Novoyatleva T, Mogha A, Monk KR, Mühlfeld C and Engel FB. Organ-specific function of adhesion G protein-coupled receptor GPR126 is domain dependent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA(ISSN#1091-6490)2013; 110 (42):16898-16903.
- Mogha A, Benesh AE, Patra C, Engel FB, Schöneberg T, Liebscher I, Monk KR. Gpr126 Functions in Schwann Cells to Control Differentiation and Myelination via G-Protein Activation. J Neurosci.(ISSN 0270-6474)2013; 33(46):17976-17985.
- Patra C,Ricciardi F, and Engel FB.The functional properties of nephronectin: an adhesion molecule for cardiac tissue engineering. Biomaterials (ISSN#0142-9612)2012;33(17):4327–4335.
- Patra C, Talukdar S, Novoyatleva T, Reddy S,Mühlfeld C, Kundu B, Kundu SC and Engel FB. Silk protein fibroin from Antheraeamylitta for cardiac tissue engineering. Biomaterials (ISSN#0142-9612)2012;33(9):2673-2680.
- Patra C, Diehl F, Ferrazzi F, van Amerongen MJ, Novoyatleva T, Schaefer L., Mühlfeld C, Jungblut B and Engel FB. Nephronectin regulates atrioventricular canal differentiation via Bmp4-Has2 signaling in zebrafish. Development (ISSN#0950-1991) 2011; 138(20):4499-4509.